Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Measles: The Silent Invader
Measles is not just a childhood illness; it’s a formidable adversary that has stood the test of time, challenging public health systems worldwide. Its ability to spread rapidly and infect large populations makes it a significant concern. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of measles, exploring its contagious nature, symptoms, prevention, and much more.

What is Measles?
Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus. It primarily affects the respiratory system and is known for its characteristic red rash. Despite being preventable through vaccination, measles continues to pose a threat, especially in areas with low immunization rates.
How Contagious is Measles?
The contagiousness of a disease is often measured by the Basic Reproduction Number, or R₀. This number indicates how many people, on average, one infected person will pass the disease to in a fully susceptible population.
| Disease | R₀ Value |
|---|---|
| Measles | 12–18 |
| Influenza (Flu) | 1.4–4 |
| Ebola | 1.5–2.5 |
| COVID-19 (Original) | 2–3 |
Table: Comparison of R₀ Values Among Different Diseases
As evident from the table, measles has an exceptionally high R₀ value, indicating its extreme contagiousness. This means that in a population without immunity, one person with measles can infect 12 to 18 others. This high transmission rate underscores the importance of vaccination and rapid response to outbreaks.
Transmission: How Does Measles Spread?
Measles spreads through respiratory droplets released when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can remain active and contagious in the air or on surfaces for up to two hours. This means that even entering a room where an infected person has been can lead to transmission. Furthermore, individuals with measles are contagious from about four days before the rash appears to four days after, allowing the virus to spread even before symptoms are evident.
Symptoms of Measles
Recognizing the symptoms of measles is crucial for early detection and preventing further spread. The disease progresses through several stages:
-
Incubation Period (10–14 days): After exposure, the virus incubates without causing any noticeable symptoms.
-
Prodromal Stage: This phase includes.
-
High fever (may spike above 104°F)
-
Cough
-
Runny nose
-
Red, watery eyes (conjunctivitis)
-
Koplik spots (tiny white spots inside the mouth)
-
-
Rash Stage: A red, blotchy rash emerges, typically starting on the face and spreading downward to the rest of the body. This rash usually lasts about a week.
-
Recovery: The fever subsides, and the rash fades, often leaving a brownish discoloration or peeling skin.
Complications Associated with Measles
While many recover from measles without issue, the disease can lead to severe complications, especially in young children, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems. These complications include:
-
Ear Infections: Occurring in about one in ten children with measles, potentially leading to hearing loss.
-
Diarrhea: Reported in less than one in ten people with measles.
-
Pneumonia: Affecting about one in 20 children with measles, pneumonia is the most common cause of death from measles in young children.
-
Encephalitis (brain swelling): Approximately one in 1,000 children with measles will develop encephalitis, which can lead to convulsions and can leave the child deaf or with intellectual disability.
-
Death: For every 1,000 children who get measles, one to three will die from respiratory and neurologic complications.
Prevention: The Role of Vaccination
Vaccination remains the most effective method to prevent measles. The Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine is safe and highly effective. Two doses of the MMR vaccine are about 97% effective at preventing measles, while one dose is about 93% effective. It’s recommended that children receive the first dose at 12–15 months of age and the second dose at 4–6 years.
High vaccination coverage leads to herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and individuals with certain medical conditions.
Recent Measles Outbreaks: A Growing Concern
Despite the availability of a vaccine, measles outbreaks continue to occur, often in communities with low vaccination rates. For instance, as of April 3, 2025, there have been 607 confirmed measles cases across 22 U.S. jurisdictions, including states such as Alaska, California, Florida, Texas, and Washington. This resurgence highlights the critical need for maintaining high vaccination rates and public awareness.
🛑 Why Is Measles Making a Comeback?
-
Vaccine Hesitancy: Misinformation and unfounded fears about vaccine safety, especially from social media, have caused many to delay or avoid immunization. This significantly contributes to the vulnerability of communities.
-
Global Travel: In our interconnected world, travelers can easily carry the virus from regions experiencing outbreaks to countries with low or declining vaccination rates.
-
Gaps in Healthcare Access: In certain underprivileged or war-torn areas, access to vaccines is still limited, leading to pockets of unvaccinated populations.
-
Decline in Routine Immunizations During COVID-19: The pandemic caused massive disruptions in routine health services, including vaccinations, giving measles a window to return.
🧒 Measles in Children vs Adults: What’s the Difference?
| Aspect | Children | Adults |
|---|---|---|
| Symptom Onset | Rapid onset | Sometimes delayed |
| Complications Risk | Higher (pneumonia, ear infections) | Higher (encephalitis, hepatitis) |
| Hospitalization | Frequent for severe cases | Often more severe if hospitalized |
| Immunity Response | May develop stronger long-term response | Depends on vaccination history |
🩺 Diagnosis: How Is Measles Identified?
To confirm a measles diagnosis, doctors often rely on:
-
Clinical symptoms like rash, fever, and Koplik spots.
-
Laboratory testing such as:
-
Measles-specific IgM antibodies
-
RT-PCR tests to detect the virus RNA
-
-
Travel history or exposure to others with measles
Early diagnosis is key to stopping outbreaks in their tracks, especially given how measles contagious it is.
🌍 Global Measles Eradication Efforts
Organizations like the WHO, CDC, and UNICEF are actively working toward global eradication of measles through:
-
Mass immunization campaigns
-
Education to counter vaccine misinformation
-
Emergency outbreak response teams
Despite progress, the world is still far from eradicating measles due to how measles contagious remains in vulnerable regions.
💡 10 Frequently Asked Questions About Measles Contagious
1. Is measles contagious before symptoms appear?
Yes, a person can spread measles 4 days before and 4 days after the rash appears.
2. How long is someone contagious with measles?
Typically, 8 days – 4 days before and 4 days after the rash.
3. Can vaccinated individuals still get measles?
Very rarely, but it’s possible if their immune response was insufficient. However, symptoms are usually milder.
4. Can measles spread through surfaces?
Yes. The virus can survive on surfaces or in the air for up to two hours.
5. How can I protect myself from this measles contagious virus?
Get vaccinated and avoid contact with unvaccinated individuals during outbreaks.
6. Is measles airborne?
Yes, it spreads through respiratory droplets in the air.
7. What if I’ve never had measles or the vaccine?
You’re highly susceptible. Consult a healthcare provider about getting the MMR vaccine.
8. Is it safe to travel during a measles outbreak?
Only if you are vaccinated. Otherwise, postpone travel.
9. Why is measles so contagious compared to other viruses?
Its R₀ value (12–18) is among the highest. It spreads rapidly and survives long in the air.
10. Does natural infection provide lifelong immunity?
Yes, typically. However, vaccination is the safer route to immunity.
🔬 Scientific Insights: Why Is Measles So Contagious?
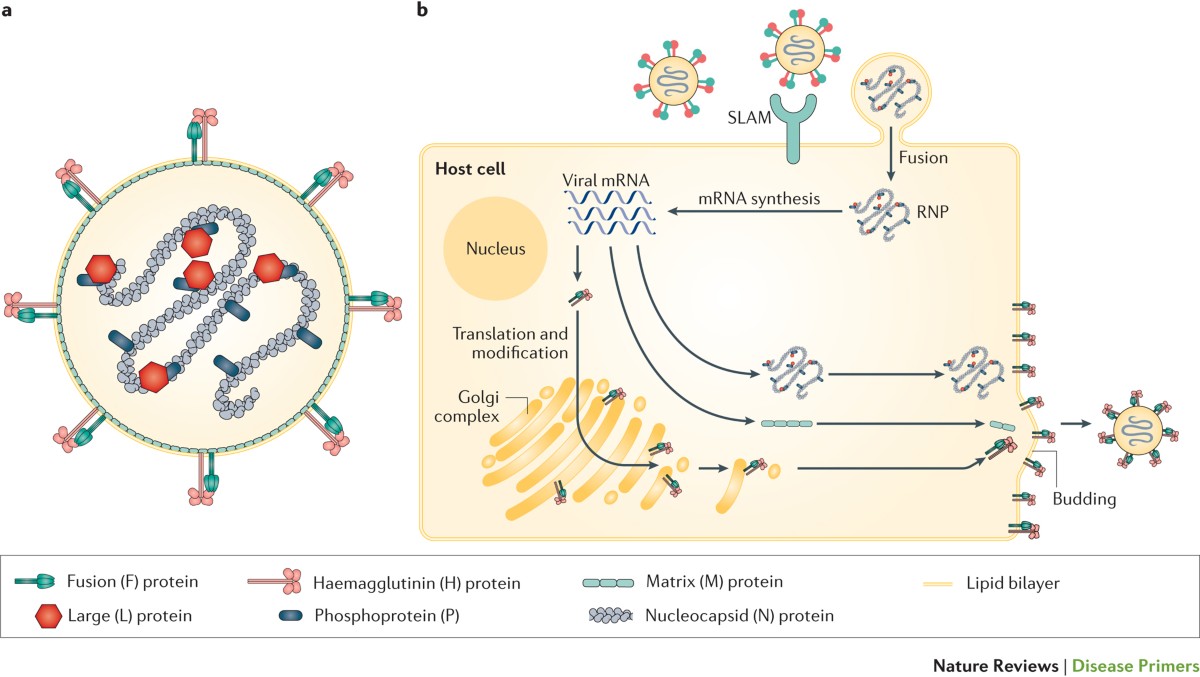
The measles virus binds to SLAM receptors on immune cells and epithelial cells. It then hijacks the host’s cellular machinery to replicate, making it incredibly efficient and fast-spreading.
It can infect 90% of unvaccinated individuals exposed to the virus — a shocking statistic that illustrates how measles contagious really is.
📈 The Impact of Vaccination on Measles Contagiousness: A Data Snapshot
| Year | Global Measles Cases | Vaccination Rate | Reported Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 853,000 | 72% | 562,000 |
| 2010 | 278,000 | 85% | 139,000 |
| 2020 | 207,000 | 84% | 60,000 |
| 2024 | 430,000 (est.) | 81% | 130,000+ (est.) |
🔔 Declining immunization rates = rising measles risk.
✅ Services for Measles Testing and Vaccination
At WeCare Health Clinics, we provide:
-
✅ Free MMR vaccinations (select locations)
-
✅ On-site measles testing (RT-PCR & antibody)
-
✅ Immunity status checkups
-
✅ Pediatric and adult consultations
-
✅ Emergency outbreak response assistance
📞 Customer Care Number: 1-800-555-9876
🌐 Visit: www.wecareclinics.com/measles
🚨 Warning Signs That Require Immediate Medical Help
Seek urgent care if you or a loved one has:
-
Difficulty breathing
-
Seizures or loss of consciousness
-
Persistent high fever
-
Dehydration symptoms (dry mouth, low urine)
🧭 Final Verdict: Is Measles Contagious?
Absolutely, yes. Measles is one of the most contagious diseases known to man. With an R₀ of 12–18 and airborne transmission, it spreads faster than many modern viruses. However, it’s also preventable with a simple, safe, and effective vaccine.
Don’t gamble with your health – protect yourself and others today.